Ntfs Reader For Mac Os
For years now, Apple has provided support for Microsoft's major drive formats—namely, FAT and NTFS. With full read and write support for FAT32, everything works well.. until NTFS support is required.
Jun 11, 2013 OS X supports the option to read NTFS-formatted drives, but has not supported writing to these drives. Therefore, the use of a third-party driver such as Paragon NTFS or Tuxera NTFS. OS X supports the option to read NTFS-formatted drives, but has not supported writing to these drives. Therefore, the use of a third-party driver such as Paragon NTFS or Tuxera NTFS has been.
Apple's native NTFS driver handles read capability, yet write support has long been absent from the equation. Even though write support is built in to the native driver itself, it's disabled by default in OS X, since Apple doesn't officially support writing data to NTFS drives.
Ntfs 3g For Mac Os Sierra
Though Apple supports exFAT, an alternative format also created by Microsoft to read/write OS X and Windows, the fact remains that Windows drives are formatted with NTFS by default. This fact makes it very likely that you'll need to write data to an NTFS-formatted drive from a Mac at some point or another. Linux reader for mac. Fingerprint reader pc.
Luckily, NTFS write access can be enabled on a per-drive basis using Apple's native driver. Remember though that this solution is unsupported, so care should be taken to properly back up data should anything go wrong, such as data corruption and/or subsequent loss.
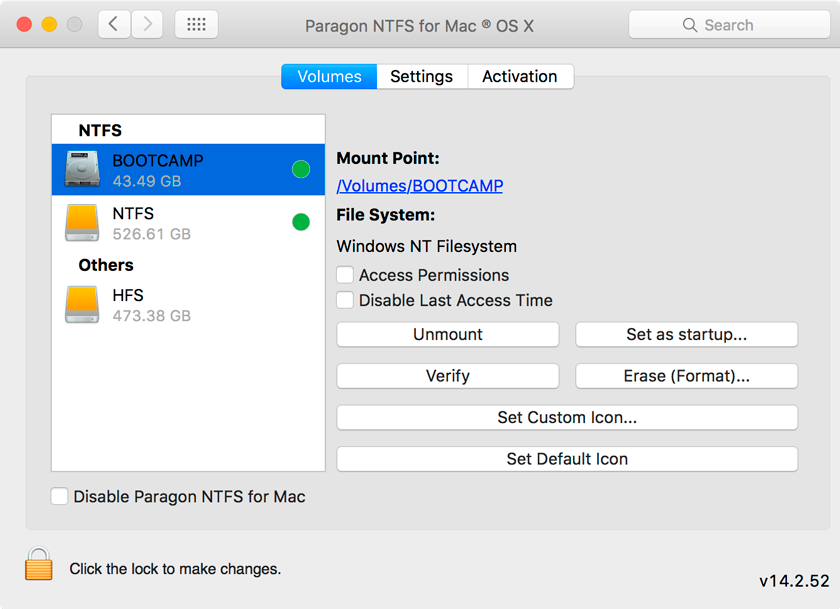
With this in mind, let's proceed.
Ntfs Reader For Mac
- On your Apple computer, connect an NFTS-formatted drive to an external port. Take note of the volume name, as you'll need it later.
- Launch Terminal.app and type in the following command, entering the admin password when prompted (Figure A).
sudo nano /etc/fstab
Figure A - This will open the fstab file that is blank by default. Now, using the volume name, enter the following command (Figure B).
LABEL=VOLUME_NAME none ntfs rw,auto,nobrowse
Figure B - Press [Ctrl]+[O] to write the information to file, then press Enter to save the change (Figure C).
Figure C - Repeat steps 2-3 for each drive you wish to enable NTFS write support on, and then press [Ctrl]+[X] to close the file (Figure D).
Figure D - Next, eject the drive(s) and mount them again. This time, you'll notice the drive does not appear in the Finder. Select Go Go to Folder.. from the Finder menu, enter /Volumes, then press Enter to view the hidden volumes connected to your Mac. From here, you'll be able to drag and drop the volume(s) to the sidebar for easy access when reading and writing to/from, as it does not mount on the desktop unfortunately.
To undo the edits made to the etc/fstab file, simply load the file (as in step 2) and delete the entries created for each drive, then save and exit. That's it!
While this is quick and easy to implement, it's not without drawbacks, such as occasional instability, the fact that it's unsupported, and you can only enable it on a per-drive basis. If you manage multiple drives, need this to work quickly and efficiently, or if you're deploying this as a solution to multiple end users, then a more robust driver like those provided by 3rd-party developers (such as FUSE or Tuxera) might be a better solution for production or mission-critical needs.